-
About us
-
-
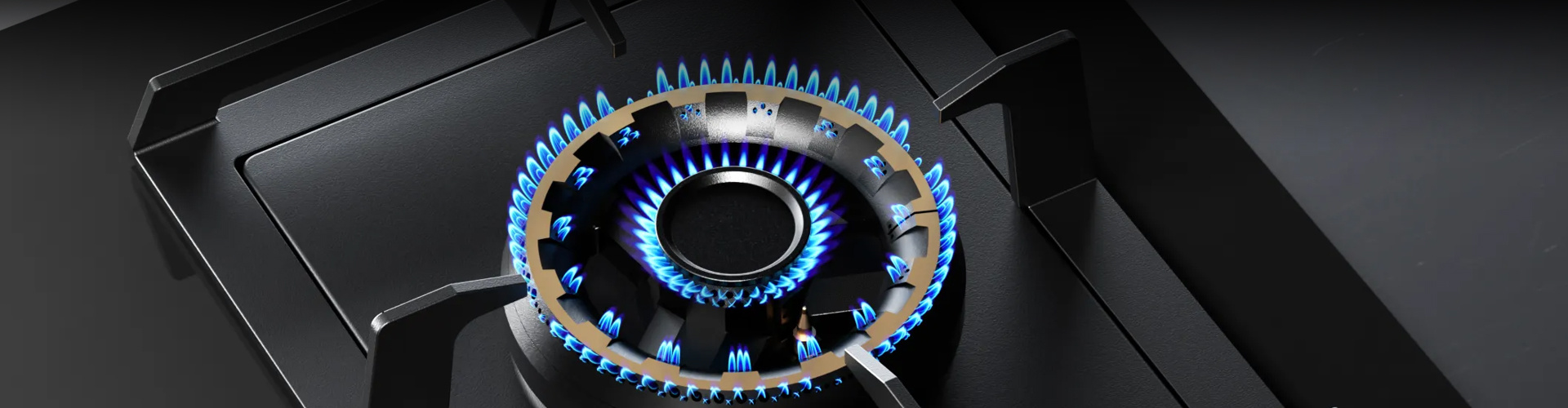

How does the flameout protection of a gas stove work?
2025-06-23
Thermocouple based flameout protection
Working principle: A thermocouple is a device that converts thermal energy into electrical energy. When the gas stove ignites, the heat of the flame will cause the thermocouple to generate a certain voltage (usually 20-30 millivolts). This voltage is transmitted to the solenoid valve, keeping it open and allowing for continuous gas supply. If the flame unexpectedly goes out, the thermocouple loses its heat source, and the generated voltage rapidly drops. The solenoid valve closes due to the loss of voltage, cutting off the gas supply and preventing gas leakage.
Advantages: Simple structure, low cost, high reliability.
Disadvantage: The reaction speed is relatively slow, and it may take a few seconds from the flame extinguishing to the complete closure of the solenoid valve.
Ionic induction flameout protection
Working principle: The ion induction flameout protection device detects ions in the flame to determine whether the flame is burning normally. When the gas stove ignites, the ions in the flame will cause the induction needle to produce a weak current. This current is transmitted to the control circuit, which determines the state of the flame based on the change in current. If the flame goes out and the ion induction needle cannot detect the current, the control circuit will immediately cut off the solenoid valve and stop the gas supply.
Advantages: Fast response speed, able to instantly detect flame extinguishing and cut off gas.
Disadvantages: Relatively high cost, sensitive to environmental humidity and impurities, and may result in misjudgment.
Thermistor based flameout protection
Working principle: Thermistor is a component whose resistance value changes with temperature. When the gas stove ignites, the heat of the flame will cause the temperature of the thermistor to rise and the resistance value to change. This change is transmitted to the control circuit, which determines the state of the flame based on the change in resistance value. If the flame goes out, the temperature of the thermistor decreases, and the resistance value returns to its initial state, the control circuit will cut off the solenoid valve and stop the gas supply.
Advantages: Simple structure, low cost, and high reliability.
Disadvantages: The reaction speed is relatively slow, and the sensitivity to temperature changes is not as good as ion induction.
Related information

Address
No. 222, Pudong Avenue ,economic Development Zone, Shaoxing, Zhejiang, China
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
COOKIES
Our website uses cookies and similar technologies to personalize the advertising shown to you and to help you get the best experience on our website. For more information, see our Privacy & Cookie Policy
These cookies are necessary for basic functions such as payment. Standard cookies cannot be turned off and do not store any of your information.
These cookies collect information, such as how many people are using our site or which pages are popular, to help us improve the customer experience. Turning these cookies off will mean we can't collect information to improve your experience.
These cookies enable the website to provide enhanced functionality and personalization. They may be set by us or by third-party providers whose services we have added to our pages. If you do not allow these cookies, some or all of these services may not function properly.
These cookies help us understand what you are interested in so that we can show you relevant advertising on other websites. Turning these cookies off will mean we are unable to show you any personalized advertising.